05Jan2018
glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels
by admin, 0 Comments
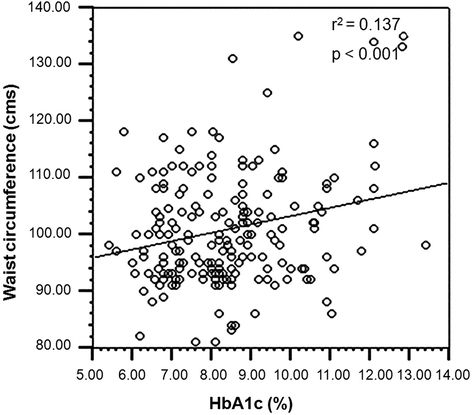
Association of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels with Iinsulin resistance in obese children.
ZE Önal, V Atasayan, T Gürbüz, E Hepkaya, C Nuhoğlu
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated the relationship between insulin resistance reflected by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR) index and serum HbA1c levels of obese children.
Material and Methods: This study included 70 obese and 60 normal weight healthy children between the ages of 3 and 15. Anthropometric measures and biochemical tests (fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HbA1c) were performed on all subjects. Plasma glucose levels were measured by the glucose oxidase method. Plasma insulin concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay (RIA). HOMA-IR index was used to estimate insulin resistance. A cut-off HOMA-IR level of ≥2.5 was accepted. The HbA1c analysis was performed using high-pressure liquid chromatography. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 5. Student’s unpaired t-test and the Mann–Whitney U test were used to determine statistical significance.
Results: Gender distribution did not reveal significant difference among the obese (F: 48.6%, M: 51.4%) and the non-obese (F: 46.7%, M: 53.3%) groups. The mean age value was significantly higher in the obese group (10.09± 3.09) (p>0.005) than the non-obese group (8.31±3.14) (p<0.05). The mean value of body mass index (BMI) was 25.55±4.3 in the obese group and 16.63±2.3 in the non-obese group. The mean HOMA-IR values of obese group (2.84±1.77) was significantly higher than the non-obese group (1.50±0.95) (p<0.005). Insulin resistance was significantly higher in the obese group. Subjects with HOMA-IR ≥2.5 levels in the obese group had significantly higher HbA1c values than those with HOMA-IR <2.5 levels.
Conclusions: High HbA1c levels in obese children can be used as a screening tool to detect insulin sensitivity and resistance at an early stage.
Key words: children, HbA1c protein, insulin resistance, obesity.
Recent Posts
- Editor’s choice: Tackling infectious diseases, NCDs and sexual reproductivehealth issues as we enter our 24th year of remarkable growth
- Preconception and contraceptive care for women living with HIV/AIDSattending antiretroviral treatment clinics in Lagos State, Nigeria
- Effects of SNPs on TNF-α and IL-10 cytokine expression in TB and HIVpatients in the Capricorn district, Limpopo Province, South Africa
- Prevalence of Schistosomiasis in a neglected community, South western Nigeria at two points in time, spaced three years apart
- Review of Leishmaniasis in the Middle East and North Africa
Recent Comments
Categories
- 2001 Issues
- 2002 Issues
- 2003 Issues
- 2004 Issues
- 2005 Issues
- 2006 Issues
- 2007 Issues
- 2008 Issues
- 2009 Issues
- 2010 Issues
- 2011 Issues
- 2012 Issues
- 2013 Issues
- 2014 Issues
- 2015 Issues
- 2016 Issues
- 2017 Issues
- 2018 Issues
- 2019 Issues
- 2024 Issues
- Articles
- December issue
- December Release
- June Issue
- June Release
- March Issue
- March Issue
- March Release
- News
- number / volume 2
- number /volume 1
- number /volume 1
- number /volume 1 2008
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2 special Issue
- number 2 special Issue 2
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number/ volume 3 2008
- number/ volume 4 2008
- number/volume 1
- number/volume 1
- number/volume 2
- number/volume 2
- number/volume 2 2008
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 4
- number/volume1
- September Issue
- September Release
- Special Edition
- special Issue
- Uncategorized
- Vol. 24 No. 1 (2024)
- volume 1
- volume 1
- volume 1
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume1
Categories
- 2001 Issues
- 2002 Issues
- 2003 Issues
- 2004 Issues
- 2005 Issues
- 2006 Issues
- 2007 Issues
- 2008 Issues
- 2009 Issues
- 2010 Issues
- 2011 Issues
- 2012 Issues
- 2013 Issues
- 2014 Issues
- 2015 Issues
- 2016 Issues
- 2017 Issues
- 2018 Issues
- 2019 Issues
- 2024 Issues
- Articles
- December issue
- December Release
- June Issue
- June Release
- March Issue
- March Issue
- March Release
- News
- number / volume 2
- number /volume 1
- number /volume 1
- number /volume 1 2008
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 1
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2
- number 2 special Issue
- number 2 special Issue 2
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 3
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number 4
- number/ volume 3 2008
- number/ volume 4 2008
- number/volume 1
- number/volume 1
- number/volume 2
- number/volume 2
- number/volume 2 2008
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 3
- number/volume 4
- number/volume1
- September Issue
- September Release
- Special Edition
- special Issue
- Uncategorized
- Vol. 24 No. 1 (2024)
- volume 1
- volume 1
- volume 1
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 2
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 3
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume 4
- volume1
